|
Some current research topics:
(1) Dual role of TRIP effect on ductility and toughness 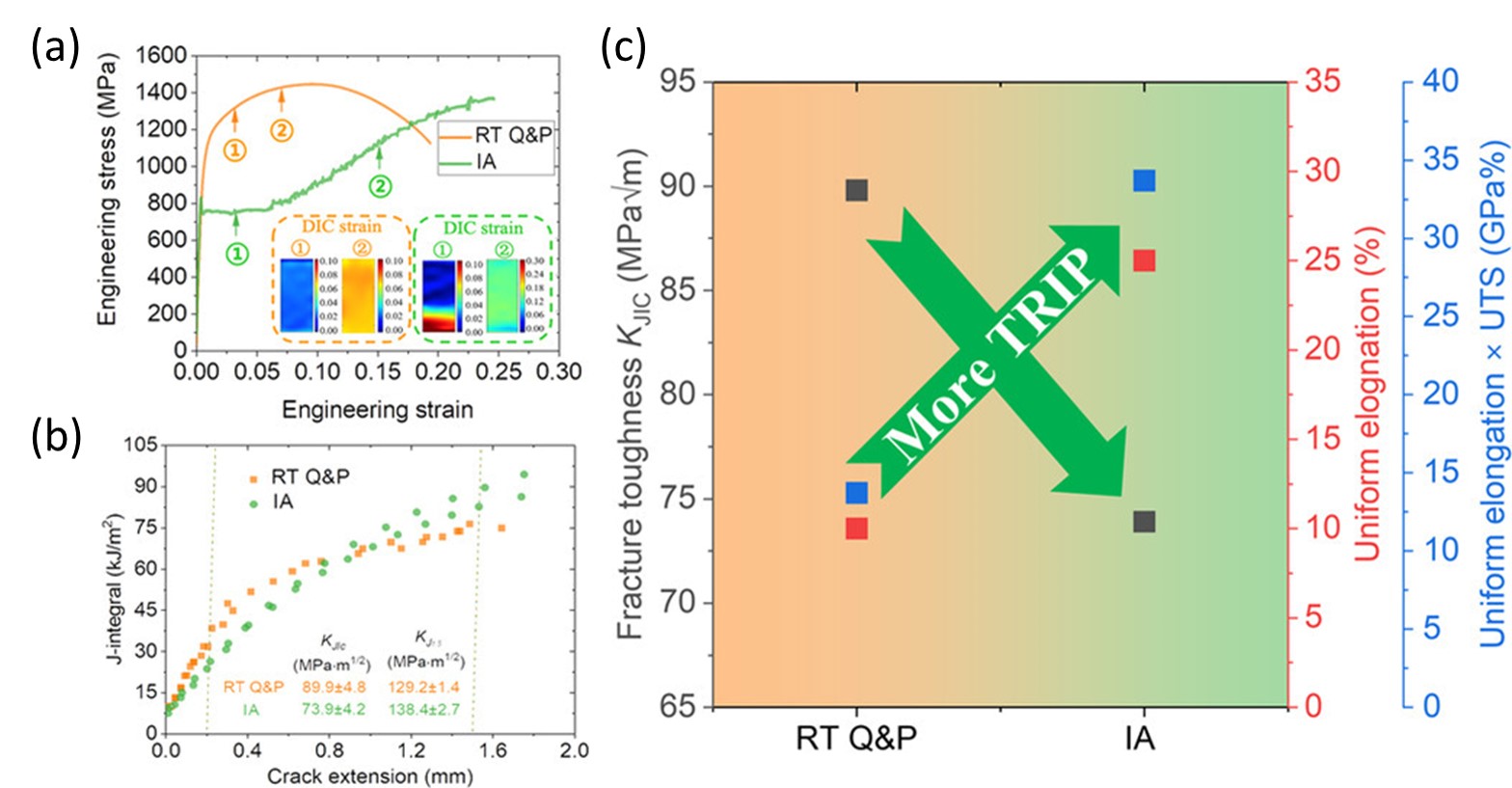 (a) Tensile stress-strain curves with DIC results of strain in the inset and (b) fracture toughness data of the IA and the RT Q&P steels ; (c) schematic diagram of the tensile and fracture properties comparison.
(2) Anti-pathogen stainless steel combating COVID-19  (a) Lift buttons made from the stainless steel SS-20Cu by PM technology. (b) Viability of the SARS-Cov-2 on the surfaces of SS-20Cu compared with other metals and alloys.
 (a) BSE image for Cu-rich precipitates of micron and submicron sizes within the stainless steel matrix; (b) the corresponding EDX mapping of Cu element.
(3) Sequential dual-passivation strategy for stainless steels 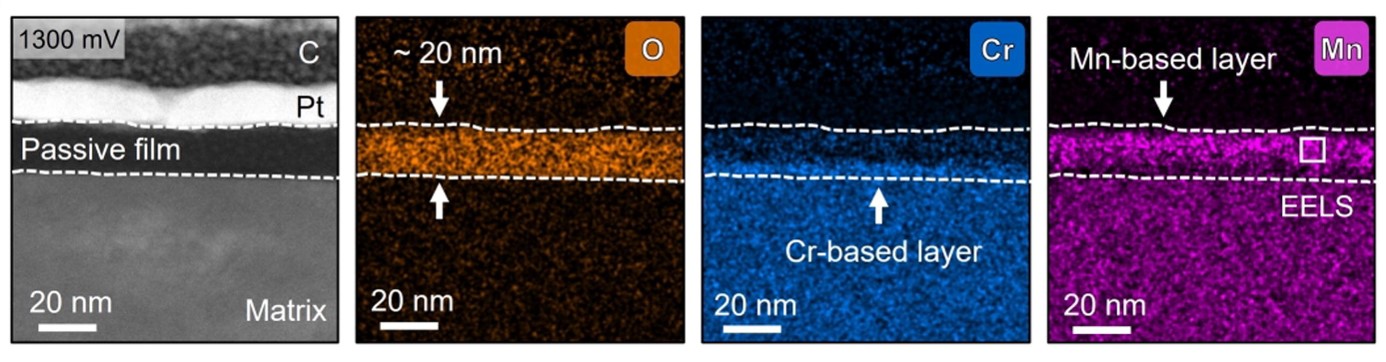 STEM-EDS identification of the Mn-SS passive film at 1300 mV(saturated calomel electrode, SCE).
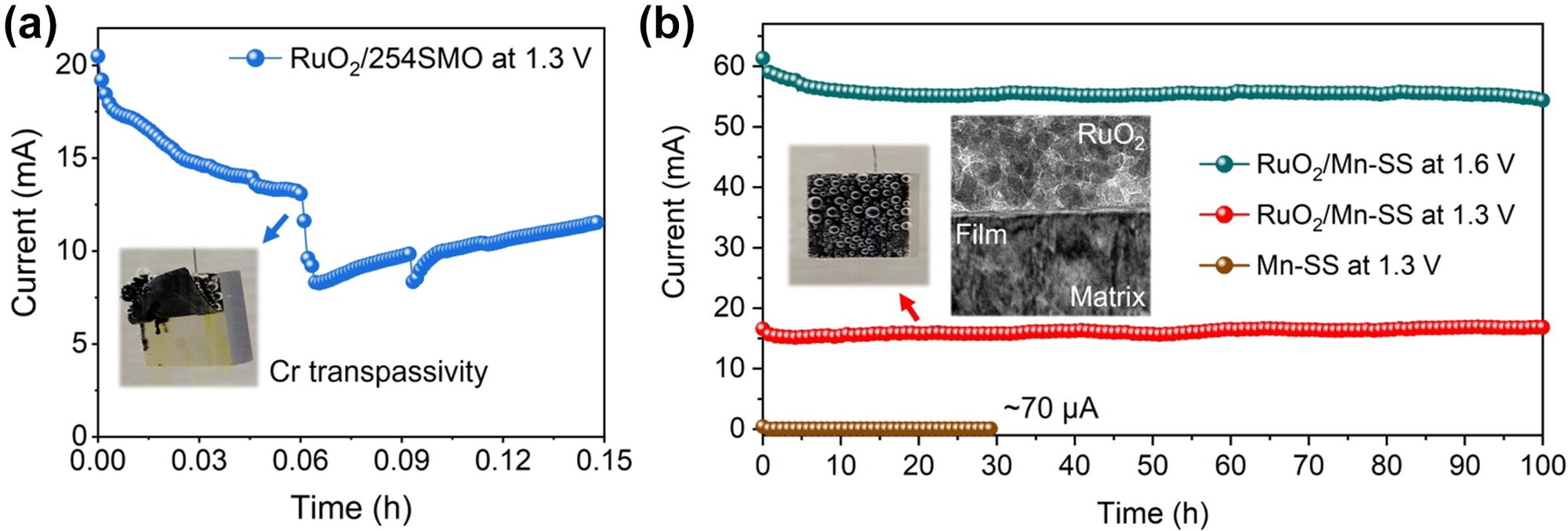 Oxygen evolution reaction (OER) stability of catalyst substrates in NaCl. (a) Potentiostatic stability measurements of the RuO2/254SMO electrode at 1300 mV(SCE);
(b) Potentiostatic stability measurements of the RuO2/Mn-SS electrode at 1300 and 1600 mV(SCE). Inserted is the TEM image of the RuO2/Mn-SS interface
at 1300 mV for one hour, showing the formation of a passive film.
(4) High strain rate deformation of alloys 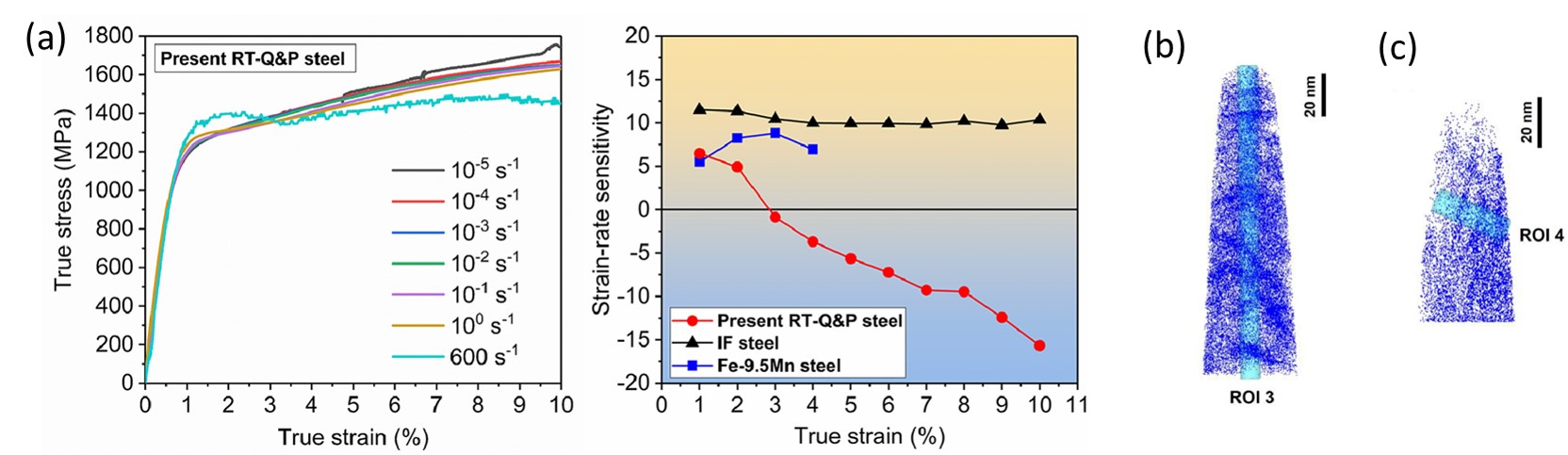 (a) Carbon-free steel (IF steel and Fe-9.5Mn steel) shows positive strain-rate sensitivity (SRS) throughout the deformation, while carbon-containing steel (present RT-QP steel) presents negative SRS after yielding;
Carbon distribution of the present RT-Q&P steel after (b) low-strain-rate and (c) high-strain-rate deformation.
.
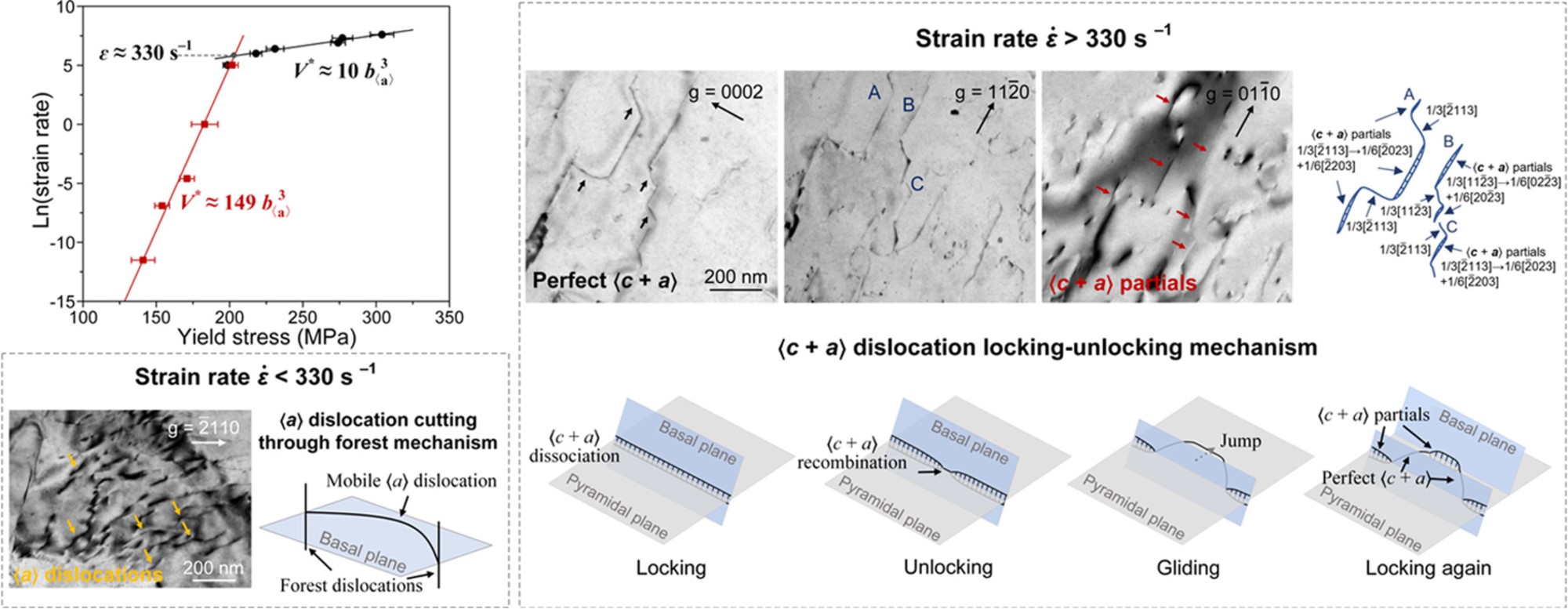 Rate-dependent transition of dislocation mechanisms in a magnesium alloy.
(5) Hydrogen embrittlement 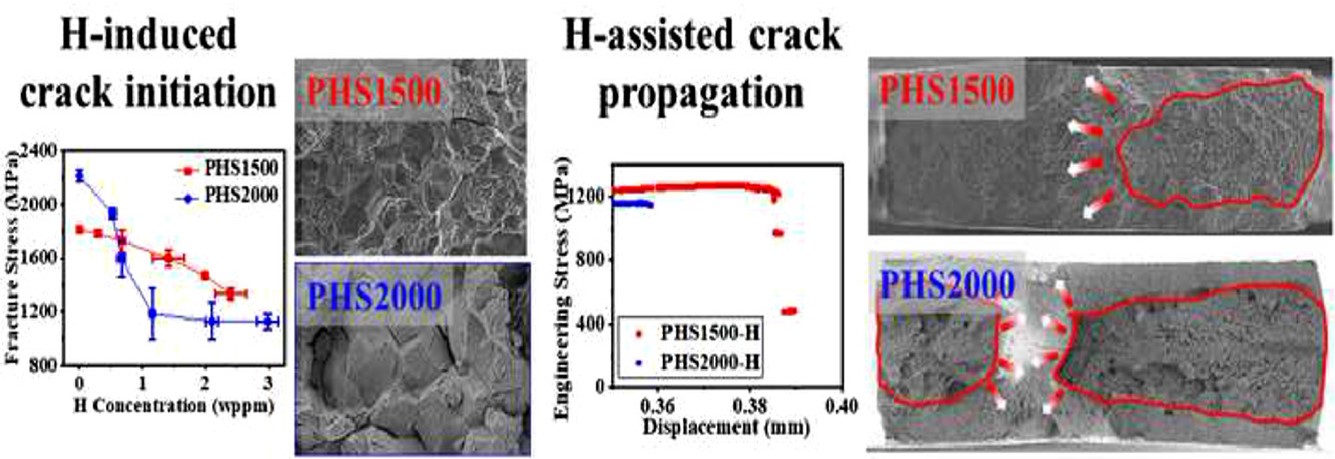 The resistance of PHS1500 and PHS2000 to hydrogen embrittlement. PHS2000 cannot offer any weight saving over PHS1500 when hydrogen content is higher than ∼0.5 wppm.
(6) Cost-effective green hydrogen 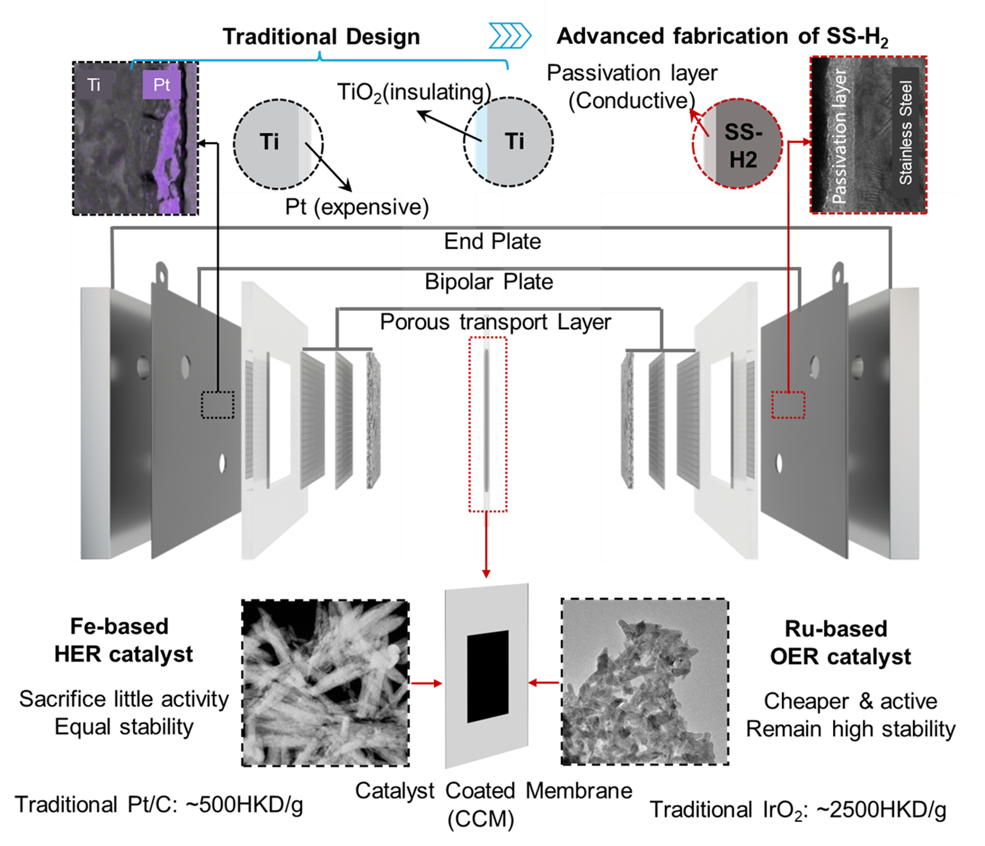 (a) Super stainless steels; (b) Advanced fabrication technology; (c) Low-cost catalytic systems.
|

|
|
Research |
_text_