New Paper: A 3D micro-printed single cell micro-niche with asymmetric niche signals – An in vitro model for asymmetric cell division study
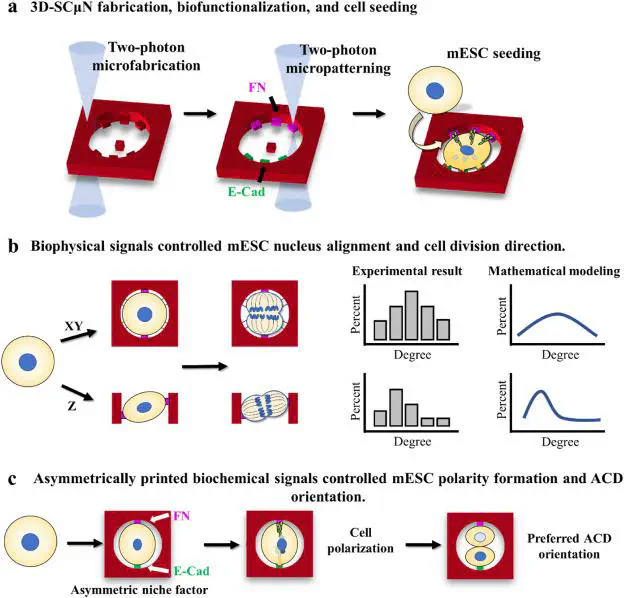
In this paper, microarrays of protein-based 3D single cell micro-niche (3D-SCµN), with precisely engineered biophysical and biochemical niche signals, are micro-printed by our multiphoton microfabrication and micropatterning technology.
Check out the published paper here: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2024.122684
Abstract
Intricate microenvironment signals orchestrate to affect cell behavior and fate during tissue morphogenesis. However, the underlying mechanisms on how specific local niche signals influence cell behavior and fate are not fully understood, owing to the lack of in vitro platform able to precisely, quantitatively, spatially, and independently manipulate individual niche signals. Here, microarrays of protein-based 3D single cell micro-niche (3D-SCµN), with precisely engineered biophysical and biochemical niche signals, are micro-printed by a multiphoton microfabrication and micropatterning technology. Mouse embryonic stem cell (mESC) is used as the model cell to study how local niche signals affect stem cell behavior and fate. By precisely engineering the internal microstructures of the 3D SCµNs, we demonstrate that the cell division direction can be controlled by the biophysical niche signals, in a cell shape-independent manner. After confining the cell division direction to a dominating axis, single mESCs are exposed to asymmetric biochemical niche signals, specifically, cell-cell adhesion molecule on one side and extracellular matrix on the other side. We demonstrate that, symmetry-breaking (asymmetric) niche signals successfully trigger cell polarity formation and bias the orientation of asymmetric cell division, the mitosis process resulting in two daughter cells with differential fates, in mESCs.